To create linked list in C/C++ we must have a clear understanding about pointer. Now I will explain in brief what is pointer and how it works.
A pointer is a variable that contains the address of a variable. The question is why we need pointer? Or why it is so powerful? The answer is they have been part of the C/C++ language and so we have to use it. Using pointer we can pass argument to the functions. Generally we pass them by value as a copy. So we cannot change them. But if we pass argument using pointer, we can modify them. To understand about pointers, we must know how computer store variable and its value. Now, I will show it here in a very simple way.
Let us imagine that a computer memory is a long array and every array location has a distinct memory location.
int a = 50 // initialize variable a
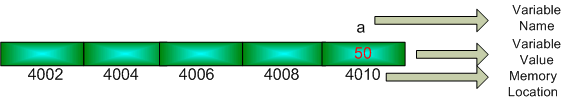
Figure: Variable value store inside an array
It is like a house which has an address and this house has only one room. So the full address is-
Name of the house: a
Name of the person/value who live here is: 50
House Number: 4010
If we want to change the person/value of this house, the conventional way is, type this code line
a = 100 // new initialization
But using pointer we can directly go to the memory location of 'a' and change the person/value of this house without disturbing ‘a’. This is the main point about pointer.
Now the question is how we can use pointer. Type this code line:
int *b; // declare pointer b
We transfer the memory location of
a to b.b = &a; // the unary operator & gives the address of an object
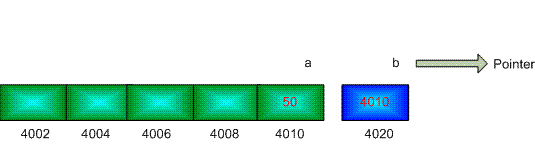
Figure: Integer pointer
b store the address of the integer variable aNow, we can change the value of
a without accessing a.*b = 100; // change the value of 'a' using pointer ‘b’ cout<<a; // show the output of 'a'
When you order the computer to access to access
*b, it reads the content inside b, which is actually the address of a then it will follow the address and comes to the house of a and read a`s content which is 50.Now the question is, if it is possible to read and change the content of
b without accessing b? The answer is affirmative. We can create a pointer of pointer.int **c; //declare a pointer to a pointer c = &b; //transfer the address of ‘b’ to ‘c’
So, we can change the value of
a without disturbing variable a and pointer b.**c = 200; // change the value of ‘a’ using pointer to a pointer ‘c’ cout<<a; // show the output of a
No comments:
Post a Comment